The Impact of BPD on Memory Loss and What To Do About It

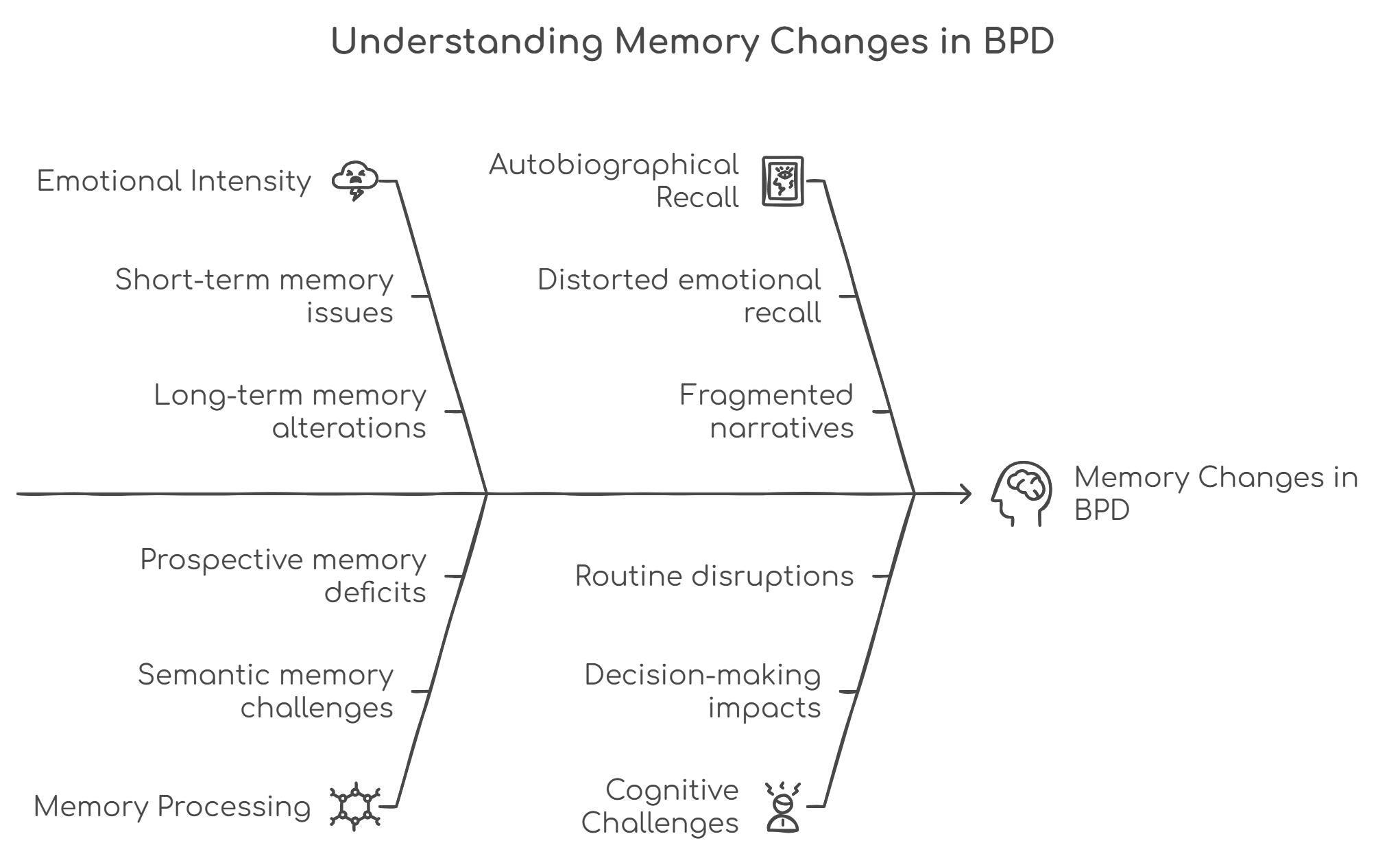
BPD can significantly disrupt your memory through emotional intensity, trauma responses, and dissociative episodes.
You’ll likely experience challenges with both short-term and long-term memory, particularly during periods of emotional dysregulation or stress.
These disruptions can affect your ability to retain new information, access stored memories, and maintain consistent autobiographical narratives.
To manage BPD-related memory loss, you can implement practical strategies like digital reminders, journaling, and structured routines, while incorporating mindfulness and grounding techniques.
Understanding how BPD affects your memory processing is the first step toward developing effective coping mechanisms and treatment approaches.
Table of Contents
BPD Memory Disruption Patterns

Your BPD-related memory disruptions follow distinct patterns, with emotional experiences significantly affecting how your brain processes and stores information.
During intense emotional states or trauma, you’re likely to experience gaps in memory through dissociative episodes, where your brain temporarily disconnects from the present moment.
These memory disruptions often manifest most strongly when you’re processing negative emotional experiences, as research shows BPD can enhance both retrograde and anterograde amnesia specifically for negative stimuli.
Emotional Memory Processing
Through the complex lens of BPD, emotional memory processing follows distinct patterns that set it apart from typical memory function.
When you’re experiencing BPD symptoms, your emotional memory encoding becomes intensified during heightened emotional states, particularly with negative experiences.
This creates an imbalance in how your brain processes and stores information.
Your emotional memory retrieval patterns show a notable bias toward negative experiences, while positive memories often become harder to access.
During emotional memory consolidation, you’ll typically experience stronger imprints of distressing events, which can overshadow neutral or positive experiences.
Discover Your Path to a Longer, Healthier Life!
Take our free quiz to see how your lifestyle measures up to the world's longest-living communities and receive expert tips for a healthier, longer life.
Take the QuizThis emotional memory disruption manifests in how you interpret past events and influences your present reactions.
The emotional memory bias you experience isn’t just about remembering negative events more vividly – it’s about how your brain prioritizes and processes emotional information differently.
You’ll notice that during periods of emotional intensity, your memory becomes more selective, focusing primarily on aspects that align with your current emotional state.
This pattern can create challenges in maintaining balanced perspectives of past experiences and relationships, particularly during times of emotional dysregulation.
BPD Memory Loss Triggers
Building on how emotional memory processing works, specific triggers can activate memory disruption patterns in BPD.
You’ll notice that negative emotional triggers particularly impact your memory recall distortion, often leading to stress-induced forgetfulness during heightened emotional states.
Research shows that your brain’s emotional stimulus processing becomes overwhelmed, causing temporary memory gaps.
| Trigger Type | Impact on Memory |
|---|---|
| Interpersonal Conflict | Immediate memory gaps and recall difficulties |
| Environmental Stress | Increased dissociative episode memories |
| Emotional Overwhelm | Distorted recall of recent events |
| Physical Exhaustion | Compromised memory formation |
Understanding these triggers helps you identify when you’re most vulnerable to memory disruptions.
During intense emotional experiences, your brain’s ability to process and store information becomes compromised, leading to fragmented memories or complete blanks.
Research indicates that stress hormones directly affect your hippocampus function, disrupting normal memory consolidation.
When you experience emotional flooding, your brain’s protective mechanisms can trigger dissociative responses, resulting in periods where memory formation becomes impaired or blocked entirely.
Recognizing these patterns enables you to implement preventive strategies before memory disruption occurs.
Dissociative Memory Gaps
Dissociative memory gaps represent a distinct pattern of memory disruption in BPD, characterized by periods where consciousness and memory formation become temporarily disconnected.
During these episodes, you’ll experience significant challenges with autobiographical memory function, making it difficult to recall personal experiences or maintain a coherent timeline of events.
When you’re experiencing dissociation related amnesia, your brain’s ability to process and store new memories becomes compromised.
This disruption particularly affects temporal sequencing impairments, where you might struggle to place events in their correct chronological order.
Memory consolidation challenges often occur during periods of emotional triggering of memory, where intense feelings can interfere with your brain’s normal memory formation processes.
You’ll notice these gaps most prominently in situations involving emotional stress or trauma.
Your memory might appear fragmented, with certain events completely missing from your recollection while others remain vivid.
Research indicates that these memory disruptions serve as a protective mechanism, but they can significantly impact your daily functioning and sense of continuous identity through time.
Trauma Impact on Memory Function
Traumatic experiences in BPD profoundly alter memory function by disrupting normal encoding and retrieval processes.
When you’re experiencing trauma-induced amnesia, your brain’s protective mechanisms can block access to specific memories, creating gaps in your recollection of traumatic events.
This disruption serves as a defense mechanism but can significantly impact your daily functioning.
You’ll notice that trauma-related dissociation often accompanies these memory disturbances, causing you to feel disconnected from your experiences and creating additional barriers to memory formation.
Trauma-based memory disruption affects both your ability to form new memories and access existing ones, particularly during periods of emotional intensity.
Your trauma-driven cognitive impairment may manifest as difficulty concentrating, processing new information, or maintaining consistent memory recall.
Understanding your trauma processing memory challenges is crucial for developing effective coping strategies.
You might experience fragmented memories, intrusive flashbacks, or periods of complete memory loss surrounding traumatic events.
Research shows that these disruptions primarily affect your episodic memory system, while your procedural memory typically remains intact.
Working with a mental health professional can help you develop techniques to manage these memory challenges effectively.
Understanding BPD Memory Changes

Your BPD can affect different types of memory simultaneously, with short-term recall becoming inconsistent during emotional episodes and long-term memories potentially fragmenting or distorting over time.
The way your brain processes and stores memories may shift dramatically when you’re experiencing intense emotions, leading to gaps in your recollection of both recent and past events.
These memory changes often manifest through difficulty retaining new information in the moment, challenges accessing stored memories accurately, and alterations in how your brain encodes experiences during periods of emotional intensity.
Short Term Memory Problems
Many individuals with BPD experience significant short-term memory difficulties, particularly during periods of emotional intensity or stress.
These challenges manifest through various working memory impairments that affect your ability to hold and process information in real-time.
You’ll notice these difficulties most prominently when trying to remember recent conversations, appointments, or daily tasks.
Research shows that short term recall deficits in BPD often coincide with autobiographical memory distortions, making it harder to accurately remember recent personal experiences.
You might struggle with semantic memory challenges, affecting your ability to retain and retrieve factual information, especially during emotionally charged situations.
Lifespan Comparison Tool
Compare the life expectancy by the U.S. State
These issues can significantly impact memory related decision making, as you may find it difficult to access and utilize recent information when making choices.
During periods of heightened emotional arousal, you’ll likely experience increased difficulty with information processing and storage.
Your working memory capacity may temporarily decrease, affecting your ability to multitask or follow complex instructions.
This pattern typically intensifies during stress, creating a cycle where emotional dysregulation further compromises your short-term memory function.
Long Term Memory Alterations
Individuals with BPD experience three distinct patterns of long-term memory alterations that fundamentally reshape how past experiences are stored and retrieved.
When you’re living with BPD, your emotional autobiographical recall becomes significantly heightened for negative experiences while positive memories often fade more quickly.
| Memory Type | Impact | Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Working Memory | Difficulty holding information | Use written lists and reminders |
| Episodic Memory | Fragmented personal narratives | Keep a detailed journal |
| Semantic Memory | Reduced fact retention | Create organized study systems |
| Prospective Memory | Missing future commitments | Set multiple digital alerts |
| Autobiographical | Distorted emotional recall | Practice mindfulness techniques |
You’ll notice that your long-term memory changes particularly affect your ability to maintain consistent narratives about your past.
Research shows these alterations stem from the way your brain processes and stores information during heightened emotional states.
Your working memory deficits can compound these issues, making it harder to transfer new experiences into long-term storage.
Understanding these patterns helps you develop targeted strategies to manage your episodic memory disruptions and improve your overall memory function.
Memory Processing Difficulties
During periods of emotional intensity, BPD significantly disrupts how the brain processes and stores new information.
You’ll find that semantic memory processing becomes particularly challenging when you’re experiencing heightened emotions, making it difficult to categorize and understand new concepts effectively.
Your prospective memory deficits may manifest as trouble remembering to complete planned tasks or follow through with future commitments, especially during periods of emotional dysregulation.
Autobiographical memory distortions can affect how you recall personal experiences, often leading to inconsistent or fragmented memories of past events.
These distortions typically intensify during stress or emotional upheaval.
Research shows that implicit memory impairments can impact your ability to learn from repeated experiences, while procedural memory disruptions might interfere with your capacity to maintain routines and perform familiar tasks automatically.
You’ll notice these effects most prominently when dealing with emotional triggers or during interpersonal conflicts.
The combination of these memory processing difficulties creates a complex pattern of cognitive challenges that can significantly impact your daily functioning, making it essential to develop targeted coping strategies and maintain consistent therapeutic support.
BPD Memory Loss Management

Managing memory challenges with BPD requires consistent implementation of practical daily strategies, such as setting digital reminders, maintaining detailed journals, and establishing structured routines.
You’ll need to pair these memory aids with targeted emotional regulation techniques, including mindfulness exercises and grounding practices that help stabilize your mental state during stressful periods.
Through regular practice of memory enhancement methods, such as cognitive training exercises and stress reduction activities, you can strengthen your ability to process and retain information more effectively.
Daily Memory Coping Strategies
Implementing effective daily memory strategies forms the cornerstone of managing BPD-related memory challenges.
You’ll need to establish a systematic approach that combines digital calendar use with structured routines to compensate for memory disruptions, particularly during emotional episodes.
Start by integrating external memory aids into your daily workflow.
Digital calendar use proves especially effective, as it provides consistent reminders and helps track appointments, medications, and important tasks.
Implement mnemonic device techniques to enhance information retention, particularly for new learning situations or important sequences of events.
Daily routine structuring is crucial – create consistent patterns for essential activities to reduce cognitive load and minimize forgetting.
You’ll benefit from organizing your environment to support memory function through environmental triggers minimization.
This includes reducing clutter, establishing designated spots for important items, and maintaining organized digital and physical filing systems.
Consider using smartphone apps designed for memory enhancement, voice recordings for important conversations, and written logs to track emotional states and their impact on your memory function.
These tools, when used consistently, can significantly improve your ability to navigate daily responsibilities despite BPD-related memory challenges.
Emotional Regulation Techniques
Through effective emotional regulation techniques, you can significantly reduce BPD-related memory disruptions and improve cognitive function.
Research indicates that consistent mindfulness practice and emotional awareness training help stabilize the amygdala-hippocampal interactions responsible for memory formation during emotional states.
To develop cognitive flexibility and maintain clearer memory function, you’ll need to implement a structured approach to emotional regulation.
Regular grounding techniques can help you stay present and process memories more effectively, while self-compassion exercises reduce the intensity of negative emotional responses that often trigger memory disruptions.
Key emotional regulation strategies that directly support memory function include:
- Progressive muscle relaxation combined with mindfulness meditation (15 minutes daily)
- Emotional temperature checks using mood tracking apps (3-4 times daily)
- Structured breathing exercises during emotional triggers (4-7-8 technique)
- Body scan meditation before challenging situations (5-10 minutes)
When you’re experiencing intense emotions, these techniques help maintain the neural pathways necessary for proper memory consolidation.
By practicing these strategies consistently, you’ll strengthen your ability to regulate emotional responses and preserve cognitive function during stress.
Memory Enhancement Methods
With consistent practice, specific memory enhancement methods can counteract BPD-related memory disruptions and strengthen cognitive retention.
Through clinician guided exercises, you’ll learn targeted techniques to improve both short-term and long-term memory functioning, particularly during emotional episodes.
Start by building memory routines that incorporate daily journaling, digital note-taking, and scheduled review periods.
You’ll need to make lifestyle adjustments that support memory function, including maintaining regular sleep patterns, reducing stress triggers, and establishing consistent daily schedules.
These changes create an environment conducive to better memory retention.
Utilize memory aid resources such as smartphone apps, written planners, and voice recorders to capture important information immediately.
Progressive memory training, developed specifically for BPD patients, can help you strengthen recall abilities through structured exercises that gradually increase in complexity.
Focus on exercises that target emotional memory processing, as this area often experiences the most significant disruption in BPD.
Work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized memory enhancement strategy that addresses your specific challenges and builds upon your existing cognitive strengths.
Professional BPD Memory Treatment
Professional treatment for BPD-related memory issues combines therapeutic memory approaches with targeted medical interventions to address both cognitive and emotional aspects of memory dysfunction.
Your treatment plan may include cognitive training methods such as memory enhancement exercises, stress reduction techniques, and specialized memory recovery programs designed specifically for BPD patients.
Through structured cognitive behavioral therapy and potentially medication support, you’ll work with mental health professionals to develop strategies that strengthen memory formation and recall while managing emotional triggers that can disrupt memory processing.
Therapeutic Memory Approaches
Memory recovery specialists employ targeted therapeutic approaches to address BPD-related memory disruptions, focusing on both cognitive rehabilitation and emotional processing techniques.
Through cognitive behavioral therapy, you’ll learn to identify thought patterns that affect memory formation while developing structured routines to enhance recall.
Mindfulness practice helps strengthen your present-moment awareness, reducing dissociative episodes that often lead to memory gaps.
Memory journaling serves as a crucial therapeutic tool, allowing you to:
- Document daily experiences systematically for future reference
- Track emotional triggers that impact memory formation
- Establish clear temporal sequences of events
- Create reliable records during periods of emotional intensity
When experiencing memory disruptions, you’ll benefit from implementing grounding techniques that help maintain cognitive clarity.
These evidence-based strategies work by anchoring you to the present moment, reducing the likelihood of dissociative states that compromise memory formation.
Your therapist will guide you through establishing structured routines that support consistent memory processing, incorporating both morning and evening reflection periods to strengthen memory consolidation and recall abilities.
Medical Intervention Options
Beyond therapeutic approaches, medical intervention plays a significant role in managing BPD-related memory disruptions.
Your healthcare provider will typically begin with a comprehensive clinical assessment to determine the severity and specific patterns of your memory issues, ensuring that pharmacological interventions are tailored to your needs.
When medication efficacy has been established through research, your doctor may prescribe specific medications to address both the underlying BPD symptoms and associated memory challenges.
While there’s no single medication specifically for BPD memory loss, certain antidepressants and mood stabilizers have shown promise in improving cognitive function and emotional regulation, which can positively impact memory retention.
Your treatment plan will likely combine therapy recommendations with medication management.
You’ll need regular check-ins to monitor progress and adjust support options as necessary.
It’s crucial to maintain open communication with your healthcare team about any side effects or changes in memory patterns.
Professional medical intervention often works best when integrated with other therapeutic approaches, creating a comprehensive treatment strategy that addresses both the neurological and psychological aspects of BPD-related memory disruptions.
Memory Recovery Programs
Specialized recovery programs form the cornerstone of professional treatment for BPD-related memory issues.
Through comprehensive memory assessment tools and structured recall exercises, these programs target specific memory deficits while accounting for emotional triggers that commonly affect BPD patients.
Multidimensional memory therapy combines cognitive and emotional approaches to strengthen your memory function.
You’ll work with specialists who’ll create personalized memory plans based on your unique patterns of memory disruption and emotional responses.
These plans typically incorporate cognitive flexibility training to help you process and retain information more effectively, even during emotional distress.
Your recovery program will likely include:
- Weekly sessions using specialized memory enhancement software
- Daily structured recall exercises targeting autobiographical memory
- Emotion regulation techniques integrated with memory training
- Regular progress assessments using standardized memory tools
Through consistent participation in these programs, you’ll develop stronger memory skills and coping strategies.
Your therapist will adjust your treatment plan based on ongoing assessments, ensuring the techniques remain effective for your specific needs.
These evidence-based approaches help rebuild your memory function while addressing the underlying emotional challenges of BPD.
Cognitive Training Methods
Professional cognitive training for BPD patients focuses in on specific mental exercises and therapeutic techniques designed to strengthen memory function while managing emotional dysregulation.
You’ll work with specialists who utilize cognitive behavioral techniques alongside neuropsychological assessments to create a tailored treatment plan.
| Training Component | Clinical Benefit |
|---|---|
| Memory Consolidation Exercises | Improves retention of neutral information |
| Emotional Processing Therapies | Reduces memory disruption during stress |
| Mindfulness Based Interventions | Enhances present-moment awareness |
| Cognitive Restructuring | Strengthens memory formation pathways |
| Neural Feedback Training | Stabilizes emotional regulation |
Your treatment program will combine these evidence-based approaches with practical applications.
You’ll learn to implement memory consolidation exercises during periods of emotional stability, while developing skills to maintain cognitive function during distress.
The program typically includes weekly sessions focused on strengthening your working memory through targeted activities.
You’ll also receive training in mindfulness-based interventions to help regulate emotional responses that can interfere with memory formation.
Regular neuropsychological assessments track your progress and allow for adjustment of therapeutic strategies as needed.
Conclusion
Like a ship’s compass finding true north, you’ll navigate BPD-related memory challenges more effectively when you understand their patterns.
Your memory isn’t broken – it’s responding to intense emotional processing.
By implementing structured recording systems, practicing mindfulness techniques, and working with mental health professionals, you’re building a reliable framework for managing these disruptions.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; with the right tools, you’ll chart a clearer course forward.

 972-393-1699
972-393-1699