Causes of Temporary Confusion and Disorientation

Prefer listening? Check out the podcast version of this article.
Imagine you’re enjoying a quiet afternoon, and suddenly a friend experiences temporary confusion, much like the odd sensation you felt during a recent illness.
It’s not uncommon for such episodes to stem from various causes, including dehydration, nutrient deficiencies, or even stress.

Sometimes, medical conditions like infections or metabolic imbalances play a significant role.
You might wonder how these diverse factors can lead to similar cognitive disruptions.
Understanding these causes is crucial, but what’s even more important is recognizing the telltale signs before they escalate into something more serious.
What are these warning signs, and how can you address them?
Table of Contents
Brain State Disruptions
You may encounter acute mental changes that manifest as sudden confusion, affecting cognitive function significantly.
These disruptions can impair memory, attention, and reasoning, leading to disorientation and compromised decision-making.
Understanding these alterations is vital for timely diagnosis and intervention to restore normal brain function.
Acute Mental Changes
When the brain’s functional equilibrium is abruptly disrupted, it can lead to acute mental changes characterized by confusion and disorientation.
You’re likely to encounter acute confusion triggers that result in rapid onset symptoms.
These symptoms might include disorientation, impaired attention, and fluctuating consciousness levels.
Acute mental changes can significantly impact mental health, often necessitating a swift response to prevent further deterioration.
Discover Your Path to a Longer, Healthier Life!
Take our free quiz to see how your lifestyle measures up to the world's longest-living communities and receive expert tips for a healthier, longer life.
Take the QuizDelirium, a common cause of acute confusion, is marked by a disturbance in attention and awareness, developing over a short period.
It’s essential to distinguish delirium from other cognitive disorders due to its unique presentation and potential for reversal once the underlying cause is addressed.
In clinical practice, urgent care interventions are vital when managing acute mental changes.
Timely recognition and treatment can mitigate adverse outcomes.
Interventions might involve stabilizing the patient physiologically, addressing potential infections, correcting metabolic imbalances, or adjusting medications.
Your swift action can prevent prolonged confusion and facilitate recovery.
Ultimately, addressing these disruptions requires a keen understanding of the factors involved and a proactive approach to treatment, ensuring the best possible patient outcomes.
Cognitive Function Impact
Although brain state disruptions can arise from various factors, their impact on cognitive function is profound and multifaceted.
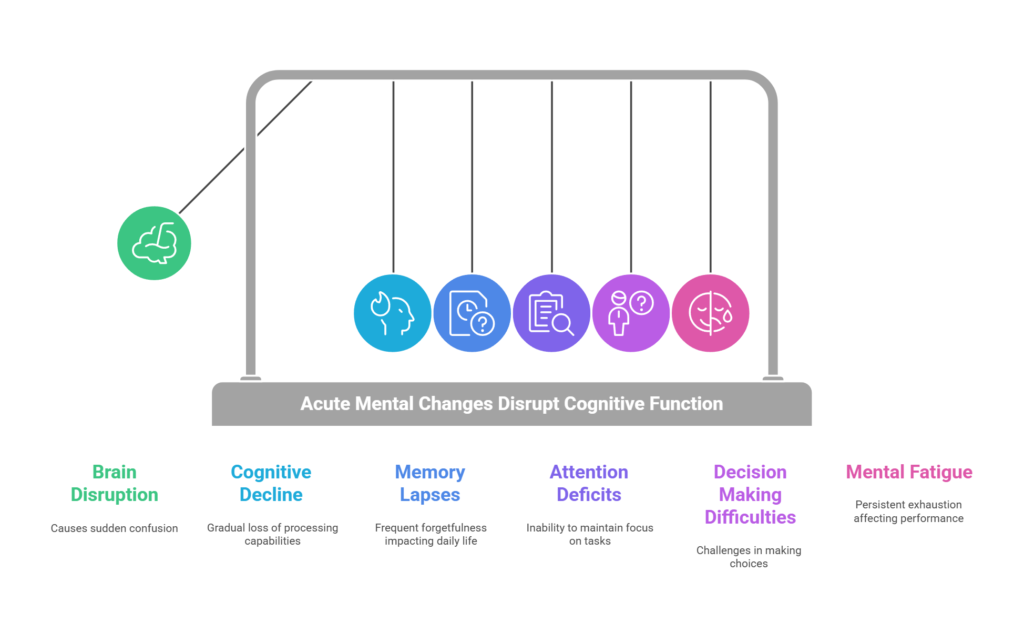
You might notice these disruptions manifest as cognitive decline, where your ability to process information gradually diminishes.
Memory lapses become more frequent, leaving you struggling to recall recent events or details.
Attention deficits might cause difficulty in focusing on tasks, leading to errors or incomplete work.
Decision making difficulties can emerge, complicating even simple choices, as your brain struggles to weigh options effectively.
Mental fatigue becomes a constant companion, making daily activities feel exhausting and overwhelming.
Consider these potential effects:
- Cognitive decline: Gradual loss of processing capabilities.
- Memory lapses: Frequent forgetfulness impacting daily life.
- Attention deficits: Inability to maintain focus on tasks.
- Decision making difficulties: Challenges in making choices.
- Mental fatigue: Persistent exhaustion affecting performance.
These symptoms not only disrupt your ability to function but also impact your quality of life.
Recognizing the signs early on is crucial.
Understanding these disruptions can empower you to seek timely intervention, potentially mitigating the progression of cognitive impairment and improving your overall well-being.
Medical Root Causes
You must consider multiple medical root causes when assessing confusion and disorientation.
Systemic health issues like liver or kidney dysfunction, neurological triggers such as seizures or transient ischemic attacks, and metabolic disturbances involving glucose or electrolyte imbalances all contribute to altered mental states.

Substance-related factors, including intoxication or medication side effects, can further exacerbate these symptoms.
Systemic Health Issues
Systemic health issues are critical medical root causes of temporary confusion, often arising from organ dysfunctions that disrupt normal physiological processes.
When these systemic conditions are present, they can lead to temporary cognitive impairments by affecting various body systems.
Systemic inflammation effects can alter brain function, as inflammatory cytokines interact with neural pathways.
Chronic disease management is crucial to prevent exacerbations that might trigger confusion.
The immune response implications from infections or autoimmune conditions can cause brain inflammation, disrupting cognitive clarity.
Organ dysfunction consequences, particularly involving the liver or kidneys, result in metabolic waste accumulation, affecting cerebral function.
Metabolic syndrome links to insulin resistance and vascular issues, which can impair cerebral perfusion and lead to disorientation.
Consider these systemic health issues:
- Systemic inflammation effects: Alters neurotransmitter activity.
- Chronic disease management: Essential to prevent exacerbations.
- Immune response implications: Can result in brain inflammation.
- Organ dysfunction consequences: Accumulation of metabolic wastes.
- Metabolic syndrome links: Compromises blood flow to the brain.
Understanding and addressing these systemic factors in medical practice is vital to mitigate the risk of temporary confusion and promote cognitive stability.
Managing systemic health issues effectively can prevent these temporary disruptions in mental clarity.
Neurological Triggers
Neurological triggers, as medical root causes, play a significant role in temporary confusion and disorientation.
When assessing these triggers, you must utilize neurological assessment techniques to evaluate cognitive function.
These techniques are essential for diagnosing conditions like non-convulsive seizures or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), which can cause sudden disorientation.
Seizure management protocols are imperative in these cases to stabilize the patient’s condition and restore cognitive clarity.
Brain imaging modalities, such as MRI or CT scans, provide crucial insights into structural or functional abnormalities in the brain.
These images can help identify areas where blood flow might be compromised, as seen in TIAs, or reveal underlying issues like head trauma or concussions.
Cognitive rehabilitation strategies may be necessary, especially for patients experiencing dementia-related disorientation.
This approach focuses on improving cognitive abilities through targeted exercises and therapies, enhancing the individual’s capacity to navigate their environment.
In managing temporary confusion from neurological causes, it’s vital to address the specific medical root cause.
By accurately diagnosing and implementing appropriate interventions, you can significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the frequency of disorientation episodes, ensuring a return to normal cognitive function.
Metabolic Disturbances
Building upon the neurological factors, it’s important to explore how metabolic disturbances can contribute to episodes of confusion and disorientation.
Metabolic syndrome implications involve complex biochemical interactions that can affect brain function, leading to cognitive impairment.
One of the most crucial aspects is the effect of glucose level fluctuations, where both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia can alter mental clarity.
Electrolyte imbalance effects, particularly concerning sodium and calcium levels, can drastically impair neuronal activity, resulting in disorientation.
Dehydration consequences shouldn’t be underestimated, as they can reduce cerebral perfusion, causing confusion.
Additionally, the nutritional deficiencies impact, especially deficiencies in essential vitamins like thiamine, can lead to significant cognitive disturbances.
To better understand these metabolic disturbances, consider the following:
- Metabolic syndrome implications can exacerbate cognitive decline.
- Glucose level fluctuations are critical triggers for confusion.
- Electrolyte imbalance effects, particularly sodium and calcium, affect mental status.
- Dehydration consequences can result in reduced cerebral perfusion.
- Nutritional deficiencies impact, such as vitamin B1 deficiency, leads to cognitive issues.
Substance-Related Factors
Substance-related factors play a pivotal role in causing temporary confusion and disorientation, often through mechanisms involving direct neurochemical alterations or withdrawal effects.
When you engage in substance misuse, your brain’s neurochemistry undergoes significant changes, leading to altered cognitive states.
Drug intoxication, whether from illicit substances or prescribed medications, can severely impair cognitive functions, resulting in confusion and disorientation.
Lifespan Comparison Tool
Compare the life expectancy by the U.S. State
Alcohol effects are particularly notorious, as acute intoxication disrupts neurotransmitter balance, while chronic misuse can lead to withdrawal symptoms, further exacerbating cognitive disturbances.
Medication interactions present another risk factor for temporary disorientation.
When you combine certain medications, especially those with central nervous system activity, unpredictable effects on cognition can occur.
These interactions can potentiate drug effects, leading to confusion or even delirium.
Withdrawal symptoms from substances like benzodiazepines or opioids can also precipitate acute episodes of confusion, as your central nervous system struggles to regain equilibrium.
Clinicians need to evaluate substance-related causes meticulously, considering both recent substance use and potential withdrawal states.
Accurate history-taking and awareness of medication interactions are crucial.
Identifying these factors promptly allows for targeted interventions, mitigating the effects on cognitive function and improving patient outcomes.
Warning Signs and Red Flags
When assessing confusion and disorientation, you’re looking for early detection markers such as sudden changes in cognitive function or difficulty concentrating.
Emergency indicators include abrupt onset of symptoms, severe disorientation, or unresponsiveness, necessitating immediate medical evaluation.
Behavioral changes, like agitation or withdrawal, and physical symptoms, such as altered gait or motor disturbances, also serve as critical red flags demanding prompt attention.
Early Detection Markers
Recognizing early detection markers for confusion and disorientation is crucial in preventing complications and ensuring timely intervention.
You must employ early identification techniques such as mental status assessments and cognitive screening tools.
These tools help detect subtle changes in cognitive function.
The importance of patient history can’t be overstated, as it provides context and reveals patterns that may indicate underlying issues.
Caregivers play a vital role through their observations, often noticing behavioral changes before they escalate.
Consider these early detection markers:
- Altered cognitive function: Look for memory lapses or difficulty concentrating.
- Behavioral changes: Agitation or withdrawal can signal cognitive disturbances.
- Disorientation: Confusion about time, place, or identity should raise concern.
- Communication difficulties: Struggles in understanding or forming coherent sentences are important indicators.
- Mood fluctuations: Sudden mood swings may suggest underlying cognitive issues.
Timely recognition of these markers allows for appropriate intervention, such as adjusting medications or addressing underlying medical conditions.
Emergency Indicators
Identifying early detection markers sets the stage for addressing more pressing concerns: emergency indicators.
When faced with temporary confusion and disorientation, you must recognize critical emergency indicators that necessitate immediate action.
These warning signs demand adherence to emergency response protocols and urgent care guidelines to mitigate potential complications.
| Warning Signs | Red Flags for Action |
|---|---|
| Sudden onset confusion | Severe disorientation |
| Incoherent speech | Lack of awareness of surroundings |
| Inability to recognize familiar faces | Unresponsiveness to stimuli |
Implementing confusion assessment tools helps differentiate between benign and alarming symptoms, guiding you toward rapid intervention strategies.
A sudden, profound change in mental status, such as incoherent speech or unresponsiveness, signals the need for critical care considerations.
These indicators should prompt immediate consultation with healthcare professionals.
Adhering to urgent care guidelines and employing rapid intervention strategies ensures timely and effective management of these dangerous symptoms.
Recognizing severe disorientation or a complete lack of awareness may indicate life-threatening conditions requiring swift response.
Prioritizing these emergency indicators allows for the initiation of appropriate medical interventions, stabilizing the patient and preventing further deterioration.
Behavioral Changes
Behavioral changes in individuals experiencing temporary confusion and disorientation serve as critical warning signs and red flags for underlying medical issues.
When you’re observing someone, take note of any sudden shifts in their demeanor or actions, as these behavioral observations can reveal much.
Communication difficulties often emerge, manifesting in an inability to articulate thoughts clearly or follow conversations effectively.
Emotional responses might become unpredictable, ranging from heightened agitation to inappropriate laughter or crying.
Social interactions can also be affected; someone may withdraw from activities they usually enjoy or exhibit unusual social conduct.
Environmental influences, such as changes in surroundings, might exacerbate these behaviors, leading to further disorientation.
You should look for specific signs that indicate a need for medical evaluation:
- Sudden changes in mood or personality
- Difficulty in maintaining coherent conversation
- Withdrawal from social settings or activities
- Increased agitation or irritability
- Reacting inappropriately to environmental stimuli
Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms accompanying temporary confusion often manifest as clear warning signs and red flags indicating underlying medical conditions.
When conducting a physical symptoms assessment, you must be vigilant for signs like abrupt changes in coordination, slurred speech, or altered consciousness levels.
These symptoms can complicate the cognitive function evaluation, making it vital to identify the precise disorientation triggers.
By analyzing these triggers, you can determine whether metabolic disturbances, neurological factors, or systemic conditions are contributing to the confusion.
During a confusion symptomatology review, pay close attention to accompanying physical signs such as fever, dehydration, or muscle weakness.
These could indicate infections or metabolic imbalances needing immediate intervention.
Behavioral response observation is crucial; noticing how individuals react to external stimuli or changes in their environment can offer insights into the severity and potential causes of their disorientation.
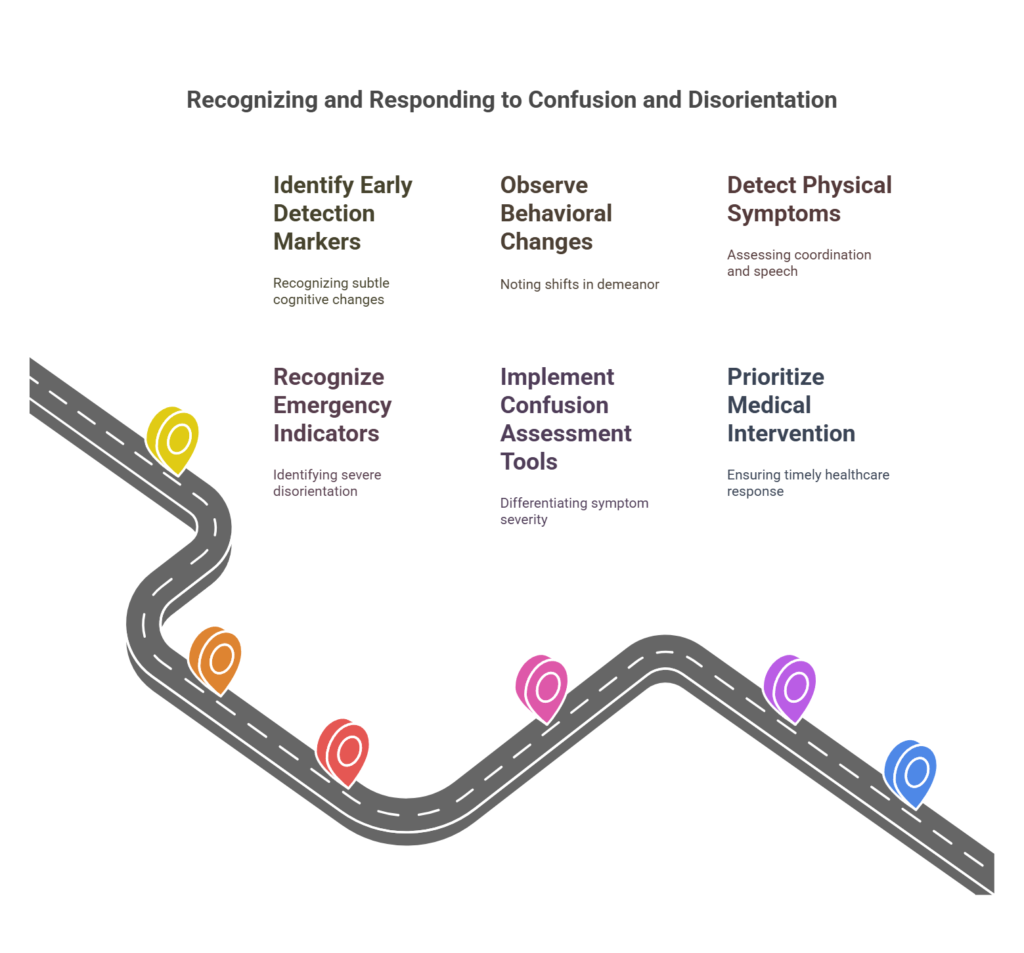
In clinical practice, recognizing these physical symptoms early can guide effective treatment strategies, ensuring that the correct underlying condition is addressed.
Recovery and Management
Your immediate response to confusion and disorientation should prioritize stabilizing the person’s environment and ensuring safety.
Treatment approaches require identifying the causative factors, which may involve targeted interventions such as medication adjustments or managing underlying medical conditions.
Prevention strategies and lifestyle adjustments, including optimizing hydration, sleep, and medication management, play crucial roles in mitigating future episodes.
Immediate Response Steps
When encountering temporary confusion, promptly assessing the situation is crucial for effective management and recovery.
Implementing immediate care involves systematic assessment protocols to ascertain the underlying cause swiftly.
Begin with rapid intervention to stabilize the condition, focusing on patient communication to ensure they comprehend your actions and intentions.
Providing caregiver support is vital to maintain a calm and reassuring environment, which can significantly aid in alleviating confusion.
Consider these essential steps:
- Evaluate Vital Signs: Check for abnormalities in pulse, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
- Monitor Neurological Status: Assess consciousness level, orientation, and ability to follow simple commands.
- Identify and Address Triggers: Look for potential causes such as dehydration, medication side effects, or recent trauma.
- Reassure and Reorient: Use clear, simple language to reassure the patient and reorient them to time and place.
- Engage Caregivers: Involve family or known caregivers to provide familiar support and context.
These immediate response steps are designed to stabilize the patient and prevent further deterioration.
Treatment Approaches
While addressing temporary confusion, it’s essential to implement targeted treatment approaches that focus on both recovery and management of the underlying cause.
Prioritize treatment efficacy by initiating therapeutic interventions tailored to the specific etiology.
This may involve medication management to correct any pharmacological imbalances contributing to the disoriented state.
Patient education is crucial in ensuring adherence to prescribed regimens and understanding potential side effects.
Regular follow-up care is necessary to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
| Treatment Aspect | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic Interventions | Tailored to specific etiology | Ensures focused recovery efforts |
| Medication Management | Corrects pharmacological imbalances | Optimizes mental clarity |
| Patient Education | Enhances adherence to treatment plans | Reduces risk of recurrence |
| Follow-up Care | Monitors progress, adjusts plans | Maintains treatment efficacy |
| Efficacy Evaluation | Assesses response to interventions | Guides ongoing clinical decisions |
Ensure that any interventions align with the identified cause, whether it’s metabolic, infectious, or neurologic.
Engage in comprehensive evaluation to refine these approaches continually.
By maintaining a clinical focus and utilizing precise terminology, you can effectively manage temporary confusion, laying the groundwork for sustained cognitive stability and improved patient outcomes.
Prevention Strategies
Implementing effective prevention strategies is fundamental in mitigating the risk of temporary confusion and promoting recovery.
Prioritizing hydration is crucial; dehydration often exacerbates cognitive dysfunction.
Ensuring sleep quality is another essential aspect, as poor sleep can significantly impact cognitive clarity and orientation.
Medication management is critical; regularly review your medication regimen to prevent adverse interactions that might contribute to confusion.
Incorporating environmental cues can aid in maintaining orientation.
Simple measures like keeping clocks and calendars visible help ground your sense of time and place.
A nutritional balance supports cognitive health, underscoring the importance of a well-rounded diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals.
To effectively prevent temporary confusion, consider the following strategies:
- Hydration Importance: Maintain adequate fluid intake to prevent cognitive decline.
- Sleep Quality: Prioritize restful sleep to support mental clarity.
- Medication Management: Regularly review medications to avoid interactions and side effects.
- Environmental Cues: Use visual aids like clocks and calendars for orientation.
- Nutritional Balance: Ensure a balanced diet to support overall brain health.
Lifestyle Adjustments
As you navigate the recovery and management of temporary confusion, adopting specific lifestyle adjustments can enhance cognitive function and overall well-being.
Implementing lifestyle changes, such as establishing healthy habits, plays a critical role in mitigating confusion episodes.
Prioritize sleep hygiene by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, avoiding stimulants before bedtime, and creating a restful environment.
Adequate rest supports optimal brain function and reduces cognitive disturbances.
Stress management is equally vital, as chronic stress can exacerbate disorientation.
Engage in relaxation techniques like mindfulness, deep breathing, or yoga to alleviate stress and promote mental clarity.
Incorporating these practices into your daily routine can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of confusion episodes.
The importance of hydration can’t be overstated.
Dehydration can lead to electrolyte imbalances, adversely impacting cognitive performance.
Ensure you consume sufficient fluids daily to maintain optimal hydration levels, thereby supporting cognitive stability.
Integrating these lifestyle modifications not only aids in the recovery from temporary confusion but also fortifies overall cognitive resilience.
By embracing these strategies, you foster a conducive environment for mental acuity, enhancing your ability to manage and recover from episodes of disorientation effectively.
Conclusion
Imagine your mind as a delicate compass, constantly guiding you through life’s journey.
When temporary confusion strikes, it’s as if a sudden storm disrupts its magnetic field, leaving you adrift.
Identifying the storm’s origin—be it a medical condition or a neurological event—is crucial to recalibrating your internal compass.
By recognizing these warning signs and addressing underlying causes, you can restore your cognitive bearings and safely navigate the complex terrain of health and wellness.

 972-393-1699
972-393-1699





